1、前言
MySQL 数据库不仅提供了数据库的服务器端应用程序,同时还提供了大量的客户端工具程序,如mysql,mysqladmin,mysqldump等等
2、工具使用
2.1 mysql 命令
Mysql命令是用的最多的一个命令工具了,为用户提供一个命令行接口来操作管理MySQL 服务器。
语法格式:
Usage: mysql [OPTIONS] [database]
1 | 例如:# mysql -uroot -p -e "select user,host from user"mysql |
大家只要运行一下“mysql –help”就会得到如下相应的基本使用帮助信息:
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysql --help |
这里主要介绍一些在运维过程中会用到的相关选项:
首先看看“-e, –execute=name”参数,这个参数是告诉mysql,我要执行“-e”后面的某个命令,而不是要通过mysql连接登录到MySQL Server 上面。此参数在我们写一些基本的MySQL 检查和监控的脚本中非常有用,运维mysql时经常在脚本中使用到它。
#mysql -hhostname -Pport -uusername -ppassword -e 相关mysql的sql语句
2.1.1 通过binlog_cache_use 以及 binlog_cache_disk_use来分析设置的binlog_cache_size是否足够
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p -e "show status like '%binlog_cache%'" |
2.1.2 通过脚本创建数据库、表及对表进行增、改、删、查操作
脚本内容如下
1 | #!/bin/bash |
2.1.2 创建授予test用户可以在指定的源登录
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p -e "grant all on *.* to 'test'@'%' identified by '123456'" |
2.1.3 测试test用户连接mysql服务器
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysql -u test -p123456 -h localhost |
2.1.4 授予脚本执行权限
1 | [root@localhost ~]# chmod +x ./mysql1.sh |
2.1.5 执行脚本
1 | [root@localhost ~]# ./mysql1.sh |
如果在连接时候使用了“-E, –vertical”参数,登入之后的所有查询结果都将以纵列显示,效果和我们在一条query 之后以“\G”结尾一样。
1 | # mysql -E -u root -p |
“-H, –html”与“-X, –xml”,在启用这两个参数之后,select出来的所有结果都会按照“Html”与“Xml”格式来输出,在有些场合之下,比如希望Xml或者Html 文件格式导出某些报表文件的时候,是非常方便的。
1 | # mysql -X -u root -p |
“–prompt=name”参数对于做运维的人来说是一个非常重要的参数选项,其主要功能是定制自己的mysql提示符的显示内容。在默认情况下,我们通过mysql登入到数据库之后,mysql的提示符只是一个很简单的内容”mysql>“,没有其他任何附加信息。非常幸运的是mysql通过“–prompt=name”参数给我们提供了自定义提示信息的办法,可以通过配置显示登入的主机地址,登录用户名,当前时间,当前数据库schema,MySQL Server 的一些信
息等等。我个人强烈建议将登录主机名,登录用户名和所在的schema 这三项加入提示内容,
因为当大家手边管理的MySQL 越来越多,操作越来越频繁的时候,非常容易因为操作的时候没有太在意自己当前所处的环境而造成在错误的环境执行了错误的命令并造成严重后果的情况。如果我们在提示内容中加入了这几项之后,至少可以更方便的提醒自己当前所处环境,以尽量减少犯错误的概率。
个人强烈建议提示符定义: “\u@\h : \d \r:\m:\s> “,显示效果:
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysql -h localhost -utest -p --prompt="\\u@\h:\\d\\r:\\m:\\s>" |
切换数据库:
1 | test@localhost:(none)10:42:52>use test_db |
提示符解释:
\u 表示用户名,
\h 表示主机名,
\d 表示当前数据库,
\r小时(12小时制),
\m分种,
\s秒,
\R The current time, in 24-hour military time (0–23)
“–tee=name”参数也是对运维人员非常有用的参数选项,用来告诉mysql,将所有输入和输出内容都记录进文件。在我们一些较大维护变更的时候,为了方便被查,最好是将整个操作过程的所有输入和输出内容都保存下来。
假如mysql命令行状态下,要进行大量的交互操作,其实可以把这些操作记录在log中进行审计,很简单mysql -u root -p –tee=/path/xxxx.log
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p --tee=/var/log/mysql.log |
也可以在服务器上的/etc/my.cnf中的[client]加入 tee =/tmp/client_mysql.log即可.
1 | [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf |
注:若没有[client]就添加即可
或者在mysql>提示符下执行下面的命令
1 | mysql> tee /tmp/my.log |
mysql其他参数选项可以通过MySQL 官方参考手册查阅,也可以通过执行“mysql –help”或man mysql得到帮助信息之后通过自行实验来做进一步的深刻认识。
2.2 mysqladmin 命令
语法:
Usage: mysqladmin [OPTIONS] command command …
mysqadmin,顾名思义,提供的功能都是与MySQL 管理相关的各种功能。如MySQL Server状态检查,各种统计信息的flush,创建/删除数据库,关闭MySQL Server 等等。mysqladmin所能做的事情,虽然大部分都可以通过mysql连接登录上MySQL Server 之后来完成,但是大部分通过mysqladmin来完成操作会更简单更方便。这里将介绍一下经常使用到的几个常用功能:
ping 命令可以很容易检测MySQL Server 是否还能正常提供服务
mysql本机上测试:
1 | [root@localhost ~]# mysqladmin -u root -p -h localhost ping |
在其他主机上测试mysql server是否正常提供服务

注1:地址192.168.56.11是mysql server的ip
注2:mysql server的防火墙要允许3306/tcp通信
注3:在mysql server上创建授权用户
status 命令可以获取当前MySQL Server 的几个基本的状态值:
mysqladmin status命令结果有下述列
| 命令结果 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Uptime | mysql服务器运行的秒数。 |
| Threads | 活跃线程的数量即开启的会话数。 |
| Questions | 服务器启动以来客户的问题(查询)数目 (只要跟mysql作交互,不管查询表,还是查询服务器状态都记一次)。 |
| Slow queries | 是慢查询的数量。 |
| Opens | mysql已经打开的数据库表的数量。 |
| Flush tables | mysql已经执行的flush tables,refresh和reload命令的数量。注:flush tables //刷新表(清除缓存) |
| reload | 重载授权表。 |
| refresh | 洗掉所有表并关闭和打开日志文件。 |
| open | 打开数据库的表的数量,以服务器启动开始。 |
| Queries per second avg | select语句平均查询时间。 |
| Memory in use | 分配的内存(只有在MySQL用–with-debug编译时可用)。 |
| Max memory used | 分配的最大内存(只有在MySQL用–with-debug编译时可用)。 |
processlist获取当前数据库的连接线程信息:
监控mysql进程运行状态:
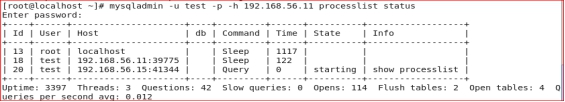
上面的这三个功能在一些简单监控脚本中经常使用到的。
mysqladmin其他参数选项可以通过执行“mysqladmin –help”或man mysqladmin得到帮助信息。
编写一个简单的mysql监控脚本,内容如下:
1 | #!/bin/bash |
附加知识点1:
Mysql的系统数据库:
1)INFORMATION_SCHEMA数据字典:此数据库存贮了其他所有数据库的信息(元数据)。元数据是关于数据的数据,如database name或table name,列的数据类型,或访问权限等。

INFORMATION_SCHEMA库的主要系统表
TABLES表:提供了关于数据库中的表和视图的信息。(Table_schema字段代表 数据表所属的数据库名)
SELECT * FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA=’数据库名’;
COLUMNS表:提供了表中的列信息。详细表述了某张表的所有列以及每个列的信息。
SELECT * FROM information_schema.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA=’数据库名‘’ AND TABLE_NAME=’表名’
TABLE_CONSTRAINTS表:存储主键约束、外键约束、唯一约束、check约束。各字段的说明信息
ELECT * FROM information_schema.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA=’数据库名’ AND TABLE_NAME=’表名’
STATISTICS表:提供了关于表索引的信息。
SELECT * FROM information_schema.STATISTICS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA=’数据库名’ AND TABLE_NAME=’表名’
2)performance_schema性能字典,此数据库为数据库性能优化提供重要的参考信息
3)MYSQL数据库: 该数据库也是个核心数据库,存储用户的权限信息与帮助信息。
4)MySQL5.7 提供了 sys系统数据库。 sys数据库里面包含了一系列的存储过程、自定义函数以及视图来帮助我们快速的了解系统的元数据信息。sys系统数据库结合了information_schema和performance_schema的相关数据,让我们更加容易的检索元数据。
附加知识点2:
mysql有关show的用法
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SHOW DATABASES | 列出 MySQL Server上的数据库。 |
| SHOW TABLES [FROM db_name] | 列出数据库中的表。 |
| SHOW TABLE STATUS [FROM db_name] | 列出数据库的表信息,比较详细。 |
| SHOW COLUMNS FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name] | 列出表的列信息,同 SHOW FIELDS FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name], DESCRIBE tbl_name [col_name]。 |
| SHOW FULL COLUMNS FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name] | 列出表的列信息,比较详细,同 SHOW FULL FIELDS FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name]。 |
| SHOW INDEX FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name] | 列出表的索引信息。 |
| SHOW STATUS | 列出 Server 的状态信息。 |
| SHOW VARIABLES | 列出 MySQL 系参数值。 |
| SHOW PROCESSLIST | 查看当前mysql查询进程。 |
| SHOW GRANTS FOR user | 列出用户的授权命令。 |
2.3 mysqldump
这个工具其功能就是将MySQL Server中的数据以SQL 语句的形式从数据库中dump 成文本文件。mysqldump是做为MySQL 的一种逻辑备份工具
2.4 mysqlbinlog
mysqlbinlog程序的主要功能就是分析MySQL Server 所产生的二进制日志(也就是binlog)。
通过mysqlbinlog,我们可以解析出binlog中指定时间段或者指定日志起始和结束位置的内容解析成SQL 语句。